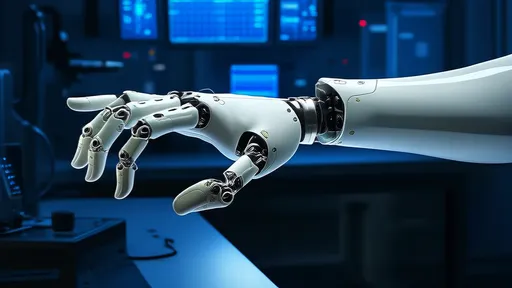
The field of prosthetics and robotics has taken a monumental leap forward with recent breakthroughs in artificial skin sensing precision. Researchers across multiple institutions have achieved unprecedented levels of tactile sensitivity in synthetic skin materials, bringing us closer than ever to replicating the remarkable sensory capabilities of human skin.
Mimicking Nature's Design
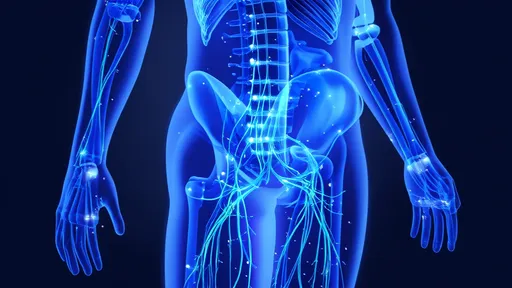
Human skin remains one of nature's most sophisticated sensory organs, capable of detecting pressure variations as subtle as a butterfly's wing. For decades, scientists have struggled to recreate this biological marvel in synthetic materials. The latest generation of artificial skin incorporates advanced nanomaterials and innovative sensor architectures that finally approach the sensitivity thresholds of biological tissue.
At the University of Tokyo, a team led by Professor Takao Someya has developed an ultra-thin, stretchable electronic skin that can measure pressure, temperature, and humidity simultaneously. What sets this material apart is its ability to maintain sensing precision even when stretched to more than twice its original size. The secret lies in a novel mesh structure of organic transistors and pressure-sensitive rubber that distributes stress evenly across the surface.
Precision That Rivals Biological Skin
Perhaps the most striking advancement comes from Stanford University, where researchers have created artificial skin that can detect pressure differences of less than 5 kilopascals - comparable to the sensitivity of human fingertips. This breakthrough was achieved through a three-layer design incorporating carbon nanotubes and specialized microstructures that amplify subtle pressure changes into measurable electrical signals.
The implications for prosthetic limbs are profound. Current prosthetic hands often rely on crude pressure sensors that provide minimal feedback. With these new high-precision artificial skins, amputees could potentially regain the ability to feel textures, judge grip strength, and perform delicate manipulations with confidence. Early clinical trials have shown remarkable results, with test subjects able to distinguish between surfaces that differ by as little as 0.2 millimeters in texture.
Beyond Medicine: Robotics Applications
While medical applications generate significant excitement, the robotics industry stands to benefit equally from these developments. Industrial robots equipped with high-precision artificial skin could handle fragile objects with unprecedented care, revolutionizing manufacturing processes in electronics, food processing, and pharmaceutical production.
German robotics company Kuka has already begun integrating prototype artificial skin modules into their next-generation collaborative robots. These sensors allow robots to detect minute changes in force during assembly operations, preventing damage to delicate components. The system can reportedly detect contact forces as small as 0.1 newtons - roughly equivalent to the weight of a sheet of paper.
Material Science Breakthroughs
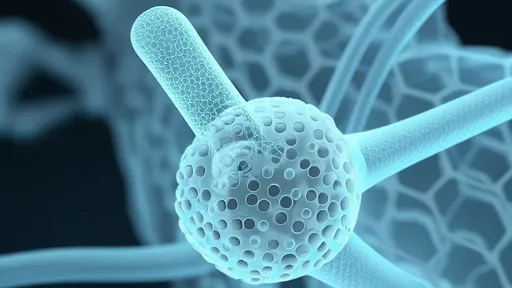
The foundation of these sensing advancements lies in novel material combinations. Researchers at MIT have pioneered a hybrid material combining graphene with a specially engineered hydrogel. This combination provides both exceptional conductivity and the mechanical properties needed for realistic tactile sensing. The graphene forms an ultra-sensitive conductive network, while the hydrogel mimics the compliance and self-healing properties of real skin.
Another promising approach comes from South Korea's Institute of Science and Technology, where scientists have developed a self-powered artificial skin that generates its own electricity from mechanical motion. Using triboelectric nanogenerators embedded in a silicone matrix, the material can detect touch without external power sources. This innovation could lead to completely autonomous sensing systems for prosthetics and robotics.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite these exciting developments, significant challenges remain. Durability under real-world conditions, manufacturing scalability, and seamless integration with neural interfaces all require further research. The most advanced artificial skins currently have operational lifetimes measured in months rather than years, and mass production of these complex materials remains costly.
Looking ahead, researchers are focusing on integrating multiple sensing modalities into single platforms. The next generation of artificial skin may combine pressure sensitivity with temperature gradients, moisture detection, and even chemical sensing - creating truly multifunctional surfaces. Several teams are also working on self-healing materials that can repair minor damage automatically, much like biological skin.
Ethical Considerations
As artificial skin approaches and potentially surpasses human capabilities in certain sensing parameters, ethical questions emerge. The potential for enhanced sensory perception raises discussions about human augmentation boundaries. Similarly, highly sensitive robotic skins could enable surveillance applications that some may find intrusive. The scientific community is beginning to address these concerns through interdisciplinary ethics panels and public engagement initiatives.
The rapid progress in artificial skin technology demonstrates how converging advances in materials science, nanotechnology, and bioengineering can solve long-standing challenges. What began as a quest to improve prosthetic devices has blossomed into a transformative technology with applications across medicine, robotics, and human-machine interfaces. As research continues, we may soon see artificial skins that not only match but enhance our natural sensory capabilities in ways we're only beginning to imagine.

By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025

By /Jul 21, 2025
By /Jul 21, 2025